Foetal Medicine
Advanced Diagnostics and Specialized Care for Your Growing Baby
Foetal Medicine Services at Freya
At Freya, our Foetal Medicine department represents the pinnacle of specialized prenatal care, treating the fetus as our primary patient. Our expert team combines cutting-edge technology with compassionate care to diagnose, monitor, and treat conditions affecting your unborn baby, ensuring the healthiest possible start to life.
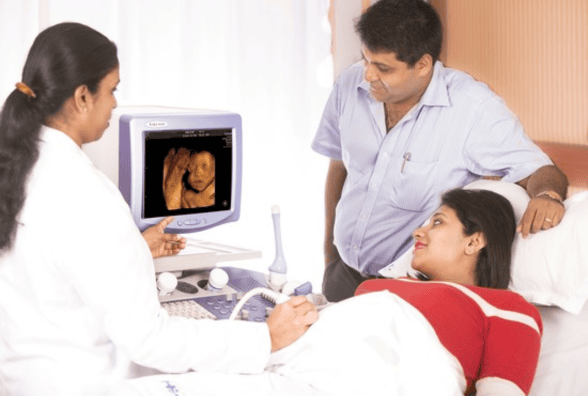
your pregnancy journey with Freya
Our Foetal Medicine Services
At Freya, we're not just delivering babies – we're nurturing families and creating positive birth experiences that last a lifetime.
Advanced Prenatal Screening
- First Trimester Screening
- Nuchal Translucency (NT) Scan
- Genetic Sonogram
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
- Preeclampsia Screening
Detailed Fetal Assessment
- TIFFA/Level II Anomaly Scan
- 4D Ultrasound Imaging
- Fetal Echocardiography
- Fetal MRI
- Doppler Studies
Specialized Diagnostic Procedures
- Amniocentesis
- Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
- Fetal Blood Sampling
- Genetic Counseling
High-Risk Pregnancy Management
- Multiple Pregnancy Care
- Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome
- Fetal Growth Restriction
- Maternal Medical Conditions
Fetal Intervention & Surgery
- Minimally Invasive Fetal Procedures
- Fetal Surgery Consultation
- Intrauterine Transfusion
- Thoracoamniotic Shunting
Conditions We Diagnose & Treat
Chromosomal Abnormalities
- Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)
- Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18)
- Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13)
- Sex chromosome abnormalities
Structural Abnormalities
- Congenital heart defects
- Neural tube defects
- Cleft lip and palate
- Limb malformations
- Kidney and urinary tract abnormalities
Complex Conditions
- Hydrops fetalis
- Skeletal dysplasias
- Metabolic disorders
- Rare genetic syndromes
One-stop for mother and child wellness
Why Choose Freya Hospital?
Freya Hospital is Ranchi’s boutique hospital for women and children—combining world-class medical expertise with the warmth, privacy, and support your family deserves.
World-Class Team: Our clinicians include highly qualified and experienced professionals such as Dr. Nidhi Nikunj (FRCOG, MRCOG), renowned for expertise in IVF, obstetrics, laparoscopy, and high-risk pregnancies.
State-Of-The-Art Facilities: Sensory labor rooms, birthing pools, hypothermia therapy, air handling units, and specialized pediatric wards.
Comprehensive Care Under One Roof: We offer a full spectrum of women’s and children’s healthcare, including gynecology, obstetrics, fetal medicine, neonatology & Level III NICU, gynecologic endoscopy, infertility and IVF, and pediatric care.
Cutting-Edge Technology: We are at the forefront with advanced treatments—offering technologies like MACS, PICSI, ICSI, Micro TESE, and more. Our modern labor rooms and NICU are meant for maximum comfort and safety.
Safe, Comfortable & Joyful Deliveries
Your Birth, Your Comfort, Our Care
At Freya Hospital, we make every delivery safe, comfortable, and joyful — supported by advanced medical expertise and a caring team by our side.
